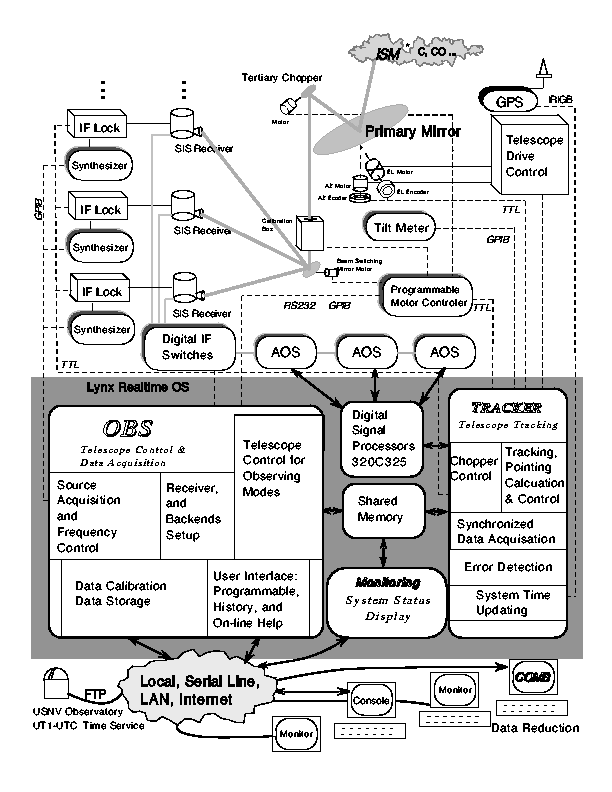
Technical Information About AST/RO

Telescope
AST/RO is a 1.7 meter diameter off-axis telescope for research in
astronomy and aeronomy at wavelengths between 200 and 2000 microns.
The instrument is now operating at the South Pole with four heterodyne
receivers and three acousto-optical spectrometers.
The AST/RO telescope was designed by Antony A. Stark of the
Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory and fabricated between 1990 and
1992 at the Scientific Instrument Facility at Boston University and at
Bell Laboratories in Holmdel, New Jersey. All the components of AST/RO
were integrated and installed at a test site at Boston University in 1993-94,
where the system was used for observations at 230 GHz and tests at 492 GHz
(Stark et al. 1994). The telescope was installed on the roof of a dedicated
support building at Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station during the 1994-95
Austral summer (Lane and Stark 1996). Astronomical observations commenced
in March 1995. The optical and mechanical properties of the telescope are
described in detail in Stark et al. (1997). Other aspects of observatory
operations are described in Stark et al. (2001).
Optics
All of the optics in AST/RO are offset to produce high beam efficiency
and to avoid inadvertent reflections and resonances.
The primary reflector is made of carbon fiber
and has an rms surface accuracy of about 9 microns. In its current
configuration, AST/RO has a Coude' focus. The telescope also has a
Nasmyth focus which is almost identical in its optical properties to
the bent Cassegrain focus on NASA's Kuiper Airborne Observatory.
Improvements in mirror alignment made in the last two years have
resulted in the following beamsizes for observations in 2001-2002:
- 230 GHz: 185''
- 460 GHz: 109''
- 492 GHz: 103''
- 806-809 GHz: 58''
Receivers
There are currently four heterodyne receivers mounted on an optical
table suspended from the telescope structure in a spacious, warm
Coude' room:
- "Major Dobbin" (230 GHz SIS receiver): 100 K DSB noise temperature.
- "Wanda" (dual 492/810 GHz SIS waveguide receiver):
460-492 GHz: 220 K DSB noise temperature;
800-820 GHz: 990 K DSB noise temperature.
(Walker et al. 1992; Honingh et al. 1997).
Simultaneous observations with the 2 mixers are possible, allowing concurrent
measurement of CO 4-3, CO 7-6, and the 809 GHz [CI] line (or alternatively,
the 492 GHz [CI] line, plus CO 7-6 and the 809 GHz [CI] line).
- "FLaMR" (460-492 GHz SIS quasi-optical receiver): 300 K DSB noise temperature
(Zmuidzinas and LeDuc 1993; Engargiola, Zmuidzinas, and Lo 1994).
- "PoleSTAR" (an array of four 800-820 GHz fixed-tuned SIS waveguide mixer receivers):
806-809 GHz: 900-950 K DSB noise temperature (Walker et al. 2001).
Spectrometers
The spectrometers currently available are: two
acousto-optical spectrometers (AOS) with
1.07 MHz resolution, 1.1 GHz bandwidth, and 2048 channels each, and one
high-resolution AOS with 44 kHz resolution, 64 MHz bandwidth, and
2048 channels (Schieder, Tolls, and Winnewisser 1989).
Operations
The entire AST/RO system is highly automated to reduce to a minimum the need
for human intervention. Observations during the Austral winter are
conducted by the AST/RO winterover scientist in residence at South Pole,
currently Dr. Chris Martin of Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
During the Austral summer (November to early February), when transportation
to South Pole is once again possible, typically 15-17 AST/RO scientists
visit the observatory to perform observations, install new instrumentation,
and maintain hardware and software. Additional information about the
system may be found in
AST/RO Technical Memorandum #35.
References
-
Engargiola, G., Zmuidzinas, J., and Lo, K.-Y. 1994, Rev. Sci. Instr., 65, 1833.
-
Honingh, C. E., Haas, S. Hottgenroth, K. Jacobs, J., and Stutzki, J. 1997,
IEEE Trans. Appl. Superconductivity, 7, 2582.
-
Lane, A. P., and Stark, A. A. 1996, Antarctic Journal of the U. S., 30(5), 337.
-
Schieder, R., Tolls, V., and Winnewisser, G. 1989, Exp. Astron., 1, 101.
-
Stark, A. A., Chamberlin, R. A., Cheng, J., Ingalls, J. G., and Wright, G., 1997,
Rev. Sci. Instr., 68, 220.
-
Stark, A. A., et al. 1994, Antarctic Journal of the U. S., 29(5), 344.
-
Stark, A. A., et al. 2001, Publ. Ast. Soc. of the Pacific, 113, 567.
-
Walker, C. K., Kooi, J. W., Chan, W., LeDuc, H. G., Schaffer, P. L.,
Carlstrom, J. E., and Phillips, T. G. 1992, Int. J. Infrared and
Millimeter Waves, 13, 785.
-
Walker, C. K., et al. 2001, Proc. of Twelfth Intern. Symp. Space THz Technology Conf., San Diego.
-
Zmuidzinas, J., and LeDuc, H. G. 1993, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theor. & Tech., 40, 1797.
System Diagram: