



Next: Stellar Observations with
Up: Examples of UVCS
Previous: Optical Signatures Related
We consider coordinated observations of coronal structures
with LASCO, to determine the directions of their magnetic fields,
and with UVCS, to measure their thermodynamical parameters.
LASCO can measure the polarization degree and direction
of the coronal [Fe XIV] ``green'' line ( 5303).
The interpretation of the linear polarization of this line
in terms of the resonance scattering/Hanle effect allows
determination of the direction of the magnetic field in the observed
coronal structure. Coordinated observations with UVCS can provide
the ion outflow velocities, the electron density,
and the proton and electron temperatures of the same structure.
The combination of these data provides the most complete set
of observational constraints to empirical models of coronal
structures.
5303).
The interpretation of the linear polarization of this line
in terms of the resonance scattering/Hanle effect allows
determination of the direction of the magnetic field in the observed
coronal structure. Coordinated observations with UVCS can provide
the ion outflow velocities, the electron density,
and the proton and electron temperatures of the same structure.
The combination of these data provides the most complete set
of observational constraints to empirical models of coronal
structures.
Interesting coordinated observations can be done with LASCO
of the green line polarization brightness, pI,
and with UVCS of the visible polarized radiance,  .
For radial magnetic fields (e.g., in the cusp of an helmet streamer),
the green line depolarization by the Hanle effect is negligible.
In this case, the ratio
.
For radial magnetic fields (e.g., in the cusp of an helmet streamer),
the green line depolarization by the Hanle effect is negligible.
In this case, the ratio  depends only on the abundance of the ion
Fe
depends only on the abundance of the ion
Fe ,
and therefore provides a method for measuring the
coronal abundance of this ion.
This method has the advantage
of being independent of collisions.
,
and therefore provides a method for measuring the
coronal abundance of this ion.
This method has the advantage
of being independent of collisions.
The ion Fe abundance can also be compared to the ion
Fe
abundance can also be compared to the ion
Fe abundance obtained by UVCS observations of the
[Fe XII]
abundance obtained by UVCS observations of the
[Fe XII] 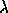 1242 line. The knowledge of two
ionization stages of the same element yields a better
determination of the ionization temperature.
1242 line. The knowledge of two
ionization stages of the same element yields a better
determination of the ionization temperature.
Coordinated Observations with UVCS and LASCO for
Coronal Magnetic Field Direction Determination

Peter Smith
Fri Jan 17 12:11:15 EST 1997
 5303).
The interpretation of the linear polarization of this line
in terms of the resonance scattering/Hanle effect allows
determination of the direction of the magnetic field in the observed
coronal structure. Coordinated observations with UVCS can provide
the ion outflow velocities, the electron density,
and the proton and electron temperatures of the same structure.
The combination of these data provides the most complete set
of observational constraints to empirical models of coronal
structures.
5303).
The interpretation of the linear polarization of this line
in terms of the resonance scattering/Hanle effect allows
determination of the direction of the magnetic field in the observed
coronal structure. Coordinated observations with UVCS can provide
the ion outflow velocities, the electron density,
and the proton and electron temperatures of the same structure.
The combination of these data provides the most complete set
of observational constraints to empirical models of coronal
structures.




 .
For radial magnetic fields (e.g., in the cusp of an helmet streamer),
the green line depolarization by the Hanle effect is negligible.
In this case, the ratio
.
For radial magnetic fields (e.g., in the cusp of an helmet streamer),
the green line depolarization by the Hanle effect is negligible.
In this case, the ratio  depends only on the abundance of the ion
Fe
depends only on the abundance of the ion
Fe ,
and therefore provides a method for measuring the
coronal abundance of this ion.
This method has the advantage
of being independent of collisions.
,
and therefore provides a method for measuring the
coronal abundance of this ion.
This method has the advantage
of being independent of collisions.
 abundance can also be compared to the ion
Fe
abundance can also be compared to the ion
Fe abundance obtained by UVCS observations of the
[Fe XII]
abundance obtained by UVCS observations of the
[Fe XII] 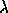 1242 line. The knowledge of two
ionization stages of the same element yields a better
determination of the ionization temperature.
1242 line. The knowledge of two
ionization stages of the same element yields a better
determination of the ionization temperature.
