Observations of scintillations of radio sources provide information on the
flow and random velocities of diffracting irregularities in the solar wind
plasma. Considering that UVCS can measure flow and random velocities
by means of Doppler
dimming and Doppler shift and line broadening techniques, coordinated UV
spectroscopy and radio measurements can provide complementary information
of the solar wind within 10 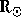 . Beyond the UVCS field of view, radio
observations can provide some additional information on the
solar wind where radio sources are present.
Since these measurements are determined by
the location of interplanetary sources, coordinated observations
with UVCS will be made in streams where IPS measurements can
be made.
. Beyond the UVCS field of view, radio
observations can provide some additional information on the
solar wind where radio sources are present.
Since these measurements are determined by
the location of interplanetary sources, coordinated observations
with UVCS will be made in streams where IPS measurements can
be made.
Interplanetary scintillation (IPS) measurements can be obtained with
EISCAT (the European Incoherent Scatter radar
system in northern Scandinavia). These measurements provide
solar wind velocities from 10 to 100 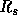 .
Additional IPS observations from the Solar Terrestrial
Environment Laboratory at Nagoya University in Japan
will be obtained.
.
Additional IPS observations from the Solar Terrestrial
Environment Laboratory at Nagoya University in Japan
will be obtained.
cm radio observations with the Very Large Array (VLA) are expected to yield the temperature, density and magnetic field strengths at the coronal base.
Photospheric magnetic field measurements (e.g. from Themis, Big Bear Solar Observatory, Kitt Peak, and the Huairou Solar Observing Station of the Beijing Astronomical Observatory in China) will yield additional constraints on the magnetic field as inferred from the cm radio observations.
Coordinated ground-based coronagraph measurements of the white light
polarization brightness and of the polarization of the coronal lines,
from Sacramento Peak, Hawaii, Pic du Midi
will be used to infer the coronal magnetic filed structure, as well
as the electron density, in the inner part of the UVCS field of view,
approximately within 2 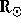 .
.
The mm radiation can provide data on the very-large scale organization of
the inner corona at least within approximately 1.3 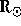 .
These data toghether with the white light images and the polarization
measurements obtained with the ground-based observations contribute to
define the coronal conditions at the base of the UVCS field of view.
.
These data toghether with the white light images and the polarization
measurements obtained with the ground-based observations contribute to
define the coronal conditions at the base of the UVCS field of view.



