



Next: Summary of Science
Up: ULTRAVIOLET CORONAGRAPH SPECTROMETER
Previous: Contents
The Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS) is an instrument
onboard the Solar and Heliospheric (SOHO) spacecraft, a joint ESA/NASA
mission to be launched in 1995.
The purpose of the UVCS is to contribute a body of data that can be used to
address a broad range of scientific questions regarding the nature of the solar
corona and the generation of the solar wind. The primary scientific goals are
the following: to locate and characterize the coronal source regions of the
solar wind, to identify and understand the dominant physical processes that
accelerate the solar wind, to understand how the coronal plasma is heated in
solar wind acceleration regions, and to increase our knowledge of the coronal
phenomena that control the physical properties of the solar wind as determined
by in situ measurements. To progress toward these goals, the UVCS will
provide ultraviolet spectroscopic measurements to be combined with
plasma diagnostic analysis techniques that are expected to lead to a far more
detailed description of the coronal plasma than presently exists. The UVCS is
intended to determine the primary plasma parameters of the solar corona from
its base to as high as 12 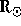 . It is expected to measure signatures
of both thermal and nonthermal processes: electron temperatures, effective
temperatures of protons and several minor ions (
. It is expected to measure signatures
of both thermal and nonthermal processes: electron temperatures, effective
temperatures of protons and several minor ions ( ,
,  ,
,
 and
and 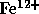 ); electron and ion densities (
); electron and ion densities ( ,
,
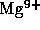 ,
,  and
and 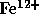 ); and flow velocities of the
electron/proton plasma and of the minor ions
); and flow velocities of the
electron/proton plasma and of the minor ions
 ,
, 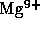 and
and  . These
measurements together with those obtained by the other coronal and
in situ experiments on SOHO should address a wide variety of
problems of solar wind physics.
. These
measurements together with those obtained by the other coronal and
in situ experiments on SOHO should address a wide variety of
problems of solar wind physics.
Peter Smith
Fri Jan 17 12:11:15 EST 1997
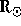 . It is expected to measure signatures
of both thermal and nonthermal processes: electron temperatures, effective
temperatures of protons and several minor ions (
. It is expected to measure signatures
of both thermal and nonthermal processes: electron temperatures, effective
temperatures of protons and several minor ions ( ,
,  ,
,
 and
and 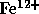 ); electron and ion densities (
); electron and ion densities ( ,
,
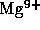 ,
,  and
and 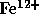 ); and flow velocities of the
electron/proton plasma and of the minor ions
); and flow velocities of the
electron/proton plasma and of the minor ions
 ,
, 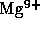 and
and  . These
measurements together with those obtained by the other coronal and
in situ experiments on SOHO should address a wide variety of
problems of solar wind physics.
. These
measurements together with those obtained by the other coronal and
in situ experiments on SOHO should address a wide variety of
problems of solar wind physics.



